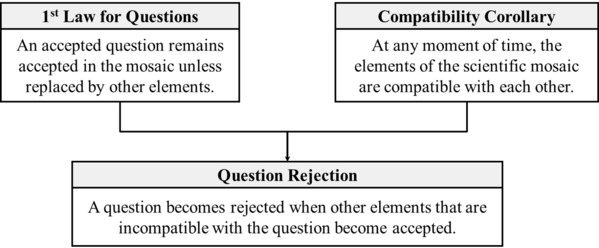
Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021)
This is an answer to the question Mechanism of Question Rejection that states "A question becomes rejected when other elements that are incompatible with the question become accepted."
This version of Question Rejection theorem was formulated by Hakob Barseghyan and Nichole Levesley in 2021.1
Contents
Scientonomic History
Acceptance Record
| Community | Accepted From | Acceptance Indicators | Still Accepted | Accepted Until | Rejection Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientonomy | 21 February 2024 | The theorem became accepted as a result of the acceptance of the respective modification. | No | 22 February 2024 | The theorem was rejected as a result of the acceptance of modification Sciento-2023-0002. It was replaced by Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-Pandey-2023). |
Suggestions To Accept
Here are all the modifications where the acceptance of this theory has been suggested:
| Modification | Community | Date Suggested | Summary | Date Assessed | Verdict | Verdict Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sciento-2021-0002 | Scientonomy | 1 August 2021 | Accept the law of question acceptance as a new scientonomic axiom, the question rejection theorem, and a number of questions for future research. | 21 February 2024 | Accepted | Prior to the 2024 workshop, Carlin Henikoff left a comment on the encyclopedia affirming that the modification should be accepted, but also stating that it was unclear whether it should be accepted as an axiom, per se. During the 2024 workshop, it was clarified that in our taxonomy, if X follows from something else, it is a theorem, but if not, it is an axiom. At the time of the publication of Levesley and Barseghyan’s paper, Henikoff was engaged in conversations in the scientonomy community about whether the law of question acceptance could be deducible from other scientonomic theorems. This clarified the thrust of her comment; since the law hasn't been shown to follow from any other scientonomic theories, it can only be taken as an axiom. There were also concerns about the phrasing of the law. Specifically, Jamie Shaw highlighted that the acceptance of a question cannot be predicated upon the acceptance of all of its presuppositions, simply because a question can have an infinite number of presuppositions. However, the participants were reminded of the difference between epistemic presuppositions and logical presuppositions (proposed by Levesley and Barseghyan in the previously accepted modification Sciento-2021-0001). While a question can have an infinite number of logical presuppositions (i.e. these are “explosive”), the law explicitly talks about epistemic presuppositions, which are not explosive. The modification was accepted nearly unanimously by over two-thirds majority of votes. 17 out of 18 votes were for acceptance. |
Suggestions To Reject
These are all the modifications where the rejection of this theory has been suggested:
| Modification | Community | Date Suggested | Summary | Date Assessed | Verdict | Verdict Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sciento-2023-0002 | Scientonomy | 28 December 2023 | Accept new formulations of the first law for theories, norms, and questions that are in tune with the formulation of the first law. Also accept new formulations of the respective rejection theorems - theory rejection, norm rejection, and question rejection. | 22 January 2024 | Accepted | During the 2024 workshop, the bulk of the discussion centered around the inclusion of the first law for norms and norm rejection theorem in the set of formulations to be accepted. Paul Patton contended that norm employment in general had not been demonstrated to be lawful beyond method employment, and our basic formulations should instead concern norm acceptance, which is patently lawful. He argued that the formulations should be modified to pertain either to methods only or to norm acceptance. It was decided that if the community were to remain uncomfortable with accepting Pandey’s new formulations, a revote would likely also need to be taken on Rawleigh’s Sciento-2022-0002, given that the issue of norm employment was also highlighted in discussions of that modification. After extensive discussion, Barseghyan suggested that the first law for norms would only apply to situations where behavior was norm-guided to begin with, which would skirt the difficulty that faces even behavioural psychologists of determining whether human behaviour in general is lawful. The majority of the community was comfortable with this workaround, and the modification was ultimately accepted with over 2/3rds majority assenting, with 11/14 votes to accept (although 1 voter voted to reject the modification and 2 voted to keep it open). |
Question Answered
Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021) is an attempt to answer the following question: How do questions become rejected? What is the mechanism of question rejection?
See Mechanism of Question Rejection for more details.
Description
TODO: Nikki add a description
Reasons
No reasons are indicated for this theory.
If a reason supporting this theory is missing, please add it here.
Questions About This Theory
The following higher-order questions concerning this theory have been suggested:
If a question about this theory is missing, please add it here.
References
- ^ Barseghyan, Hakob and Levesley, Nichole. (2021) Question Dynamics. Scientonomy 4, 1-19. Retrieved from https://scientojournal.com/index.php/scientonomy/article/view/37120.